Holographic Art: The Future of Visual Expression
In an era where technology and creativity intertwine, holographic art emerges as a groundbreaking medium that challenges our perception of reality and expands the boundaries of visual expression. This innovative art form combines cutting-edge technology with artistic vision, creating immersive experiences that blur the lines between the physical and digital worlds. As holographic art gains momentum in galleries, public spaces, and even personal devices, it's reshaping how we interact with and consume art in the 21st century.
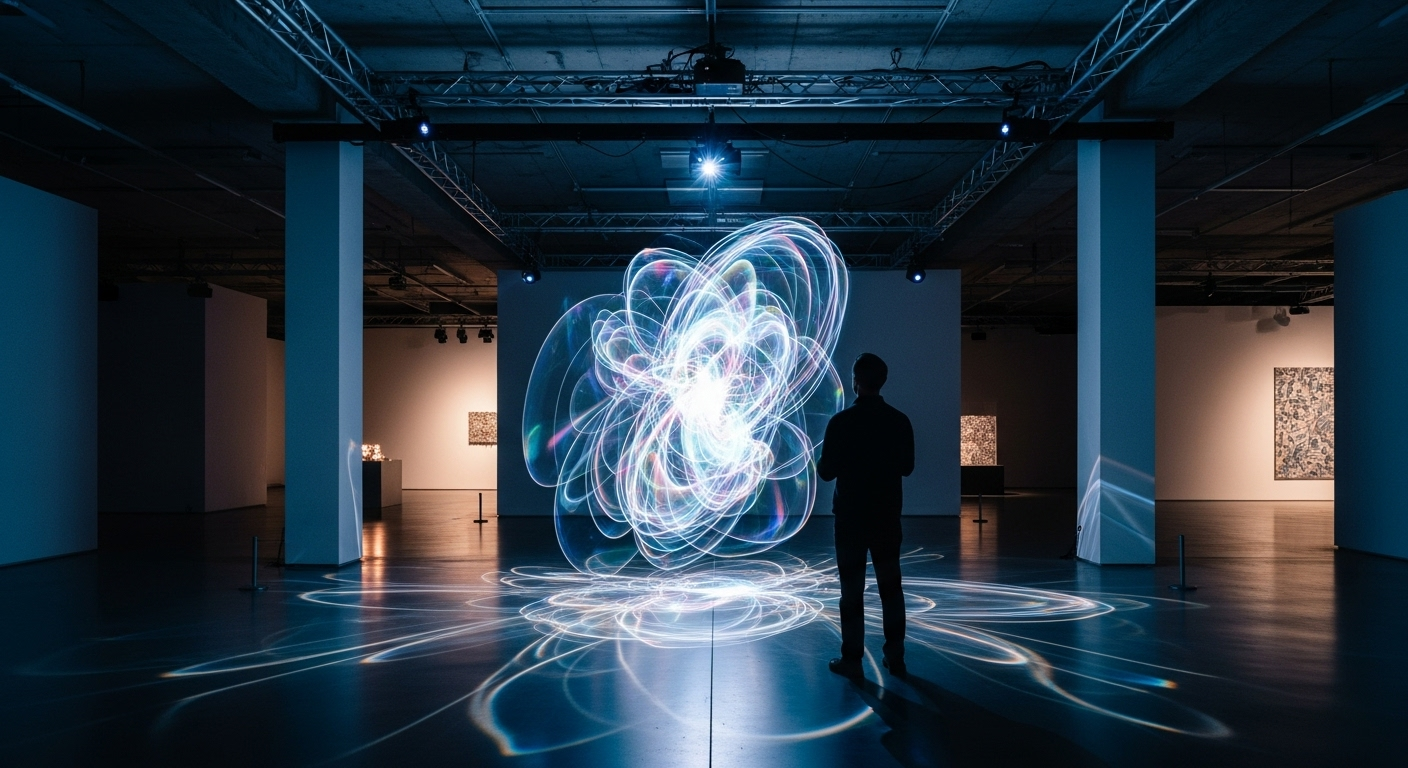

Technological Advancements Driving Holographic Art
The evolution of holographic art has been closely tied to technological progress. Early holograms were static and required specific lighting conditions to be viewed. Today, advancements in laser technology, computer processing power, and display systems have revolutionized the field. Modern holographic art can be dynamic, interactive, and visible under various lighting conditions. The development of digital holography and computer-generated holograms has further expanded the possibilities, allowing artists to create complex, animated holograms that were previously impossible.
Artistic Possibilities and Techniques
Holographic art offers unique creative possibilities that traditional mediums cannot match. Artists can create floating, three-dimensional images that viewers can walk around and observe from different angles. Some techniques allow for the creation of multi-layered holograms, where different images or scenes appear as the viewer moves. Interactive holographic installations can respond to audience movements or inputs, creating participatory art experiences. The medium also allows for the exploration of light, color, and space in ways that challenge our perceptions and create optical illusions.
Notable Holographic Artists and Works
Several contemporary artists have gained recognition for their innovative use of holographic technology. Japanese artist Hiro Yamagata has created large-scale holographic installations that transform public spaces. His Quantum Field X3 project at the 2005 Venice Biennale used laser technology to project holographic images onto the facade of the Palazzo Ducale. American artist Matthew Schreiber is known for his immersive holographic environments that combine light, space, and geometry. His work Light Topology explores the intersection of art, science, and technology through complex holographic constructions.
The Impact on Art Galleries and Museums
Holographic art is transforming the way galleries and museums present exhibitions. Traditional concerns about preservation and security are less relevant with holographic displays, allowing for more dynamic and flexible curation. Some institutions are experimenting with holographic recreations of fragile or rare artworks, enabling visitors to experience pieces that would otherwise be inaccessible. The immersive nature of holographic installations also offers new ways to engage audiences and create memorable experiences, potentially attracting younger, tech-savvy visitors to art spaces.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its potential, holographic art faces several challenges. The technology required for high-quality holographic displays remains expensive, limiting access for many artists and institutions. There are also technical limitations, such as the need for controlled lighting environments and the difficulty of capturing holographic art in photographs or videos for documentation and promotion. Some critics argue that the technological aspect of holographic art can overshadow its artistic merit, leading to works that prioritize spectacle over substance. Additionally, there are ongoing debates about the authenticity and originality of holographic reproductions of traditional artworks.
The Future of Holographic Art
As technology continues to advance, the future of holographic art looks promising. Researchers are developing more compact and affordable holographic display systems, which could make the medium more accessible to a wider range of artists and venues. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning may lead to more sophisticated interactive holographic experiences. Some experts predict that holographic art could become a common feature in public spaces, transforming urban environments into dynamic, ever-changing galleries. The potential for holographic art in virtual and augmented reality applications also opens up new possibilities for creating immersive, borderless art experiences.
Educational and Commercial Applications
Beyond the art world, holographic technology is finding applications in education and commerce. Museums are using holographic displays to create interactive educational exhibits that bring historical figures or scientific concepts to life. In the commercial sector, companies are exploring holographic advertising and product displays as a way to capture consumer attention in increasingly crowded marketplaces. These applications not only demonstrate the versatility of holographic technology but also provide potential funding sources for further artistic and technological development in the field.
Conclusion
Holographic art represents a fascinating convergence of art and technology, offering new ways to create, experience, and interact with visual content. As the medium continues to evolve, it challenges our traditional notions of art and pushes the boundaries of creative expression. While holographic art is still in its relative infancy, its potential to transform the art world and beyond is immense. As more artists embrace this technology and as it becomes more accessible, we can expect to see increasingly innovative and thought-provoking holographic works that redefine the landscape of contemporary art.